The Director-General of the Ghana Health Service (GHS), Dr Patrick Kuma-Aboagye, has revealed that five cases of monkeypox have been reported in the Eastern, Western and Greater Accra regions.
Dr Patrick Kuma-Aboagye made this revelation at a press briefing today, Wednesday, June 8 2022.
This announcement comes after the Ghana Health Service (GHS) earlier debunked claims of monkeypox detection in the country.
In a latest development, the Ghana Health Service says it has recorded five cases of monkeypox out of the 12 suspected cases.
According to Dr Patrick Kuma-Aboagye, no death has occurred among the reported cases.
“So far since the outbreak in Europe occurred, we tested 12 suspected cases in Ghana since 24 May. Currently, we have confirmed five cases in three regions – Eastern, Western and Greater Accra – this is where we discovered the five cases, no death has occurred among the cases here,” he said.
“One of the cases has been recorded in a Ghanaian who travelled to the US from Ghana, he might have picked it from here,” Dr Patrick Kuma-Aboagye told pressmen.
There are now about 237 confirmed and suspected cases of monkeypox worldwide.
The UN Health agency have announced plans to contain the monkeypox virus.
Key facts about monkeypox:
Vaccines used during the smallpox eradication programme also provided protection against monkeypox. Newer vaccines have been developed of which one has been approved for the prevention of monkeypox
Monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae.
Monkeypox is usually a self-limited disease with symptoms lasting from 2 to 4 weeks. Severe cases can occur. In recent times, the case fatality ratio has been around 3–6%.
Monkeypox is transmitted to humans through close contact with an infected person or animal, or with material contaminated with the virus.
Monkeypox virus is transmitted from one person to another by close contact with lesions, body fluids, respiratory droplets and contaminated materials such as bedding.
Monkeypox is a viral zoonotic disease that occurs primarily in tropical rainforest areas of central and west Africa and is occasionally exported to other regions.
An antiviral agent developed for the treatment of smallpox has also been licensed for the treatment of monkeypox.
The clinical presentation of monkeypox resembles that of smallpox, a related orthopoxvirus infection which was declared eradicated worldwide in 1980. Monkeypox is less contagious than smallpox and causes less severe illness.
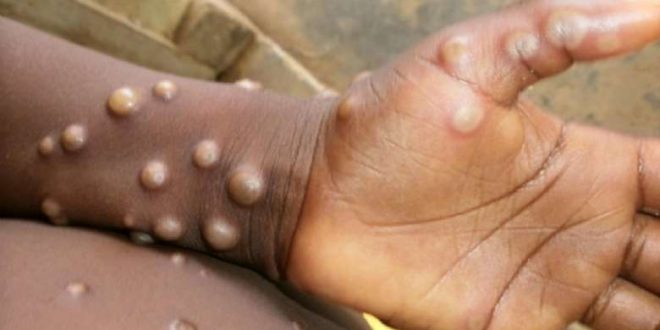
Monkeypox typically presents clinically with fever, rash and swollen lymph nodes and may lead to a range of medical complications.
—with files from WHO
Source: MyGhanaMedia.com

Send your news stories to myghanamedia@gmail.com and Chat with us via WhatsApp on +233 200818719
 MYGHANAMEDIA.COM Best Source Of Latest News
MYGHANAMEDIA.COM Best Source Of Latest News